Understanding PTSD

Understanding PTSD
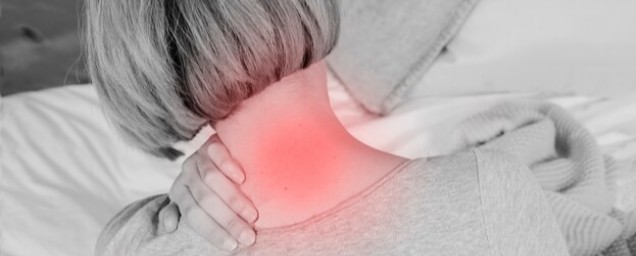
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that arises after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. These events can vary widely, from combat and natural disasters to serious accidents and personal assaults. Understanding PTSD involves not only recognizing its symptoms but also exploring its causes, how it affects individuals, and the various treatment options available. This comprehensive overview aims to provide a detailed look into PTSD, offering insights into its multifaceted nature and effective strategies for management.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD can develop following exposure to any event that is perceived as life-threatening or that severely challenges one's sense of safety. Here are some common causes:
- Combat Exposure:
- Military personnel who experience combat are at high risk for PTSD due to the extreme stress and life-threatening situations they face. The constant threat of danger and witnessing injuries or deaths can have profound psychological impacts.
- Physical or Sexual Assault:
- Victims of physical or sexual assault often develop PTSD. The violation of personal boundaries and the fear of harm or death during these events can lead to lasting trauma.
- Accidents:
- Serious accidents, whether car crashes, industrial accidents, or severe falls, can trigger PTSD. The sudden and unexpected nature of these events can leave individuals feeling vulnerable and fearful.
- Natural Disasters:
- Experiencing natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods can lead to PTSD. The loss of property, displacement, and witnessing the destruction and suffering around them can be overwhelming.
- Childhood Trauma:
- Childhood abuse, neglect, or witnessing domestic violence can result in PTSD. Early life trauma can disrupt normal development and leave long-lasting psychological scars.
Symptoms of PTSD
PTSD symptoms can vary in intensity and presentation but generally fall into four categories:
- Intrusive Memories:
- Individuals with PTSD often experience recurrent, unwanted memories of the traumatic event. This can include vivid flashbacks, where they feel as though they are reliving the trauma, and distressing dreams or nightmares.
- Avoidance:
- To manage their distress, individuals with PTSD may avoid places, people, or activities that remind them of the trauma. This avoidance can extend to discussing the event, which might lead to social withdrawal and isolation.
- Negative Changes in Thinking and Mood:
- PTSD can cause negative alterations in thoughts and emotions. Individuals might have distorted beliefs about themselves or others, such as feelings of guilt or blaming themselves for the trauma. They might also experience persistent feelings of fear, anger, or sadness, and lose interest in activities they once enjoyed.
- Changes in Physical and Emotional Reactions:
- Symptoms in this category include being easily startled, feeling tense or on edge (hyperarousal), having difficulty sleeping, and experiencing irritability or outbursts of anger. These reactions are often referred to as hypervigilance.
Impact of PTSD
The impact of PTSD extends beyond the individual, affecting their relationships, work, and daily life. Here’s how:
- Relationships:
- PTSD can strain relationships with family and friends. The affected individual might withdraw, have difficulty expressing emotions, or become irritable and angry, making it challenging to maintain healthy connections.
- Work and School:
- The symptoms of PTSD, such as difficulty concentrating, increased absenteeism, and heightened stress, can interfere with job performance or academic responsibilities, potentially leading to job loss or academic decline.
- Daily Life:
- The pervasive anxiety and emotional distress associated with PTSD can hinder daily activities, leading to a decreased quality of life. Individuals might struggle with maintaining routines, engaging in social activities, or even completing basic self-care tasks.
Treatment Options for PTSD
While PTSD can be a severe condition, various effective treatment options are available:
- Psychotherapy:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
- CBT is a common treatment for PTSD that helps individuals identify and challenge distorted thoughts and beliefs related to the trauma. Techniques such as exposure therapy, where patients are gradually exposed to trauma-related memories in a safe environment, can reduce the distress associated with these memories.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR):
- EMDR involves guided eye movements that help reprocess traumatic memories, reducing their emotional impact. This method is particularly effective for individuals who struggle with vividly intrusive memories and flashbacks.
- Medications:
- Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are often prescribed to help manage symptoms of PTSD. These medications can alleviate depression and anxiety, making it easier for individuals to engage in therapy.
- Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care:
- Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can significantly impact the management of PTSD symptoms. Physical activity, in particular, helps reduce anxiety and improve mood through the release of endorphins.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can also be beneficial in managing stress and promoting emotional well-being.
- Support Groups:
- Joining a support group for PTSD can provide a sense of community and understanding. Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others who have similar experiences can be incredibly validating and supportive.
Conclusion
PTSD is a mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and knowing the available treatment options are crucial steps toward managing and overcoming this disorder. With appropriate therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support, individuals with PTSD can lead fulfilling and productive lives. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, seeking professional help is an important step towards healing and recovery.
Articles
Build your awareness and get inspired with our researched articles on how you can strengthen your well-being
Popular Topics
An OTP has been sent to the email address
provided.
Please check your Inbox and Spam folders.

What Would You Like to Speak with a Specialist About?
Mental Fitness Journey starts Now!
Chearful Connects you with Top-tier Qualified Wellness specialists for the Price of a cup of Coffee!

Next Steps
- A Client Team member will reach out to you to schedule a session with the most suitable specialist.
- You will receive an email with a 10% Discount Code* for your 1st session.
- We invite you to Explore the Platform & Sign Up today! *Upto a maximum of $10 discount on a session purchased




 1576 Read
1576 Read

.jpg)