Safeguarding Children's Mental Health Against Abuse

Safeguarding Children's Mental Health Against Abuse
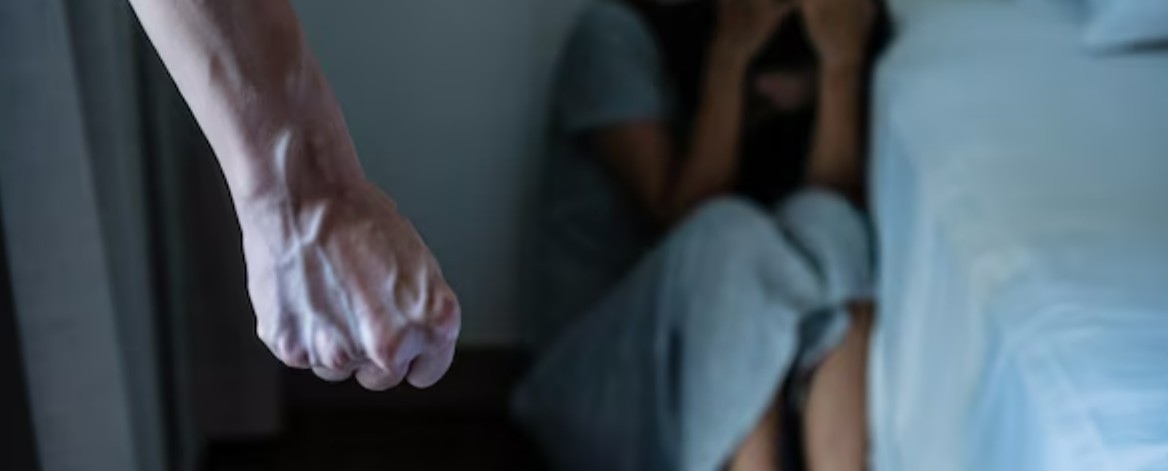
As we observe National Child Abuse Prevention Month, it's imperative to shine a light on the pervasive issue of child abuse and its profound impact on mental health. Child abuse takes many forms, each with devastating consequences that can reverberate into adulthood. Understanding the types of abuse, their effects on mental health, and strategies for prevention is crucial in safeguarding the well-being of our children.
Types of Abuse and Their Effects on Mental Health:
Child abuse encompasses various forms, including physical, emotional, sexual, and neglect. Each type inflicts profound trauma on the young psyche, leaving lasting scars that can manifest in complex ways throughout life.
Physical abuse involves the infliction of physical harm or injury on a child, often through acts of violence or punishment. This can lead to physical injuries, but the emotional toll is equally severe, resulting in feelings of fear, mistrust, and low self-esteem. Children who experience physical abuse may develop anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adulthood.
Emotional abuse, sometimes referred to as psychological abuse, involves the manipulation, belittlement, or degradation of a child's emotions and self-worth. Constant criticism, threats, or rejection can erode a child's sense of identity and security, leading to profound emotional trauma. The long-term effects of emotional abuse may include chronic anxiety, depression, and difficulty forming healthy relationships.
Sexual abuse involves any form of sexual exploitation or coercion inflicted upon a child. The psychological impact of sexual abuse can be devastating, leading to feelings of shame, guilt, and worthlessness. Survivors often struggle with intimacy issues, self-destructive behaviours, and profound trauma that can persist into adulthood, affecting their mental health and relationships.
Neglect, while often less visible, is no less damaging. It involves the failure to provide for a child's basic needs, including food, shelter, medical care, and emotional support. Chronic neglect can lead to feelings of abandonment, low self-esteem, and attachment disorders. Children who experience neglect may struggle with trust issues, substance abuse, and poor mental health outcomes later in life.
Mental Health Effects
The impact of child abuse on a child's mental health is profound and long-lasting. Children who experience abuse are at a higher risk of developing conditions such as:
Anxiety: Abuse can leave children feeling constantly on edge, worried about their safety and well-being.
Depression: The negative emotions and sense of worthlessness associated with abuse can lead to feelings of hopelessness and depression.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Children who experience severe abuse may develop PTSD, characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety related to the trauma.
Low self-esteem: Constant criticism and emotional abuse can damage a child's self-image, leading to feelings of inadequacy and worthlessness.
Substance abuse: As a way to cope with the emotional pain, children who are abused are more likely to turn to drugs or alcohol later in life.
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs):
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) refer to traumatic events or circumstances experienced during childhood, including abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. ACEs have been linked to a host of negative health outcomes, including mental health disorders, substance abuse, and chronic diseases.
Research shows that individuals with a higher number of ACEs are more likely to experience poor mental health outcomes and engage in risky behaviours. Preventing and addressing ACEs is essential in promoting resilience and mitigating the long-term impact of childhood trauma on mental health.
Ways to Protect Children and Their Mental Health from Abuse:
Protecting children from abuse requires a multifaceted approach that involves collaboration between families, communities, and policymakers. Here are some strategies to safeguard children's mental health and prevent abuse:
1. Education and Awareness: Promote awareness about the signs and consequences of child abuse among parents, caregivers, educators, and the community at large. Provide resources and training on how to recognize and report suspected cases of abuse.
2. Strengthening Families: Support families by providing access to parenting resources, counselling services, and financial assistance. Strengthening family bonds and resilience can reduce the risk of abuse and create a nurturing environment for children to thrive.
3. Empowering Children: Teach children about body autonomy, boundaries, and consent from a young age. Encourage open communication and empower children to speak up if they feel unsafe or uncomfortable. Provide age-appropriate education about personal safety and how to seek help.
4. Access to Support Services: Ensure access to comprehensive support services for children who have experienced abuse, including counselling, medical care, and legal advocacy. Invest in trauma-informed care that addresses the unique needs of survivors and promotes healing and recovery.
5. Prevention Programs: Implement evidence-based prevention programs in schools, communities, and healthcare settings to educate children, parents, and professionals about preventing child abuse. These programs can teach positive parenting strategies, promote healthy relationships, and empower bystanders to intervene.
6. Mandatory Reporting and Accountability: Enforce mandatory reporting laws and hold perpetrators of abuse accountable for their actions. Create systems for timely intervention and investigation of suspected cases of abuse to ensure the safety of children.
7. Advocacy and Policy Change: Advocate for policies and legislation that prioritize the protection of children and allocate resources for prevention and intervention efforts. Support initiatives that address the root causes of child abuse, such as poverty, inequality, and lack of access to resources.
By prioritizing the mental health and well-being of children and implementing comprehensive prevention strategies, we can create a safer and more nurturing environment where every child can thrive.
Articles
Build your awareness and get inspired with our researched articles on how you can strengthen your well-being
Popular Topics
An OTP has been sent to the email address
provided.
Please check your Inbox and Spam folders.

What Would You Like to Speak with a Specialist About?
Mental Fitness Journey starts Now!
Chearful Connects you with Top-tier Qualified Wellness specialists for the Price of a cup of Coffee!

Next Steps
- A Client Team member will reach out to you to schedule a session with the most suitable specialist.
- You will receive an email with a 10% Discount Code* for your 1st session.
- We invite you to Explore the Platform & Sign Up today! *Upto a maximum of $10 discount on a session purchased




 1729 Read
1729 Read































